|
Home | Gallery | Physik | Philosophie | Software | Musik | Kunst | H.Wacker | Links | Inhalt |
 English
English

|
|
|
| Mathematik | Linear Algebra | Geometric Algebra | Clifford Algebra | Hypercomplex Numbers | Prime Numbers |
Exponential Function: y = ex
Taylor Series of the Exponential Function
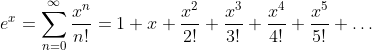
Even Part of the Exponential Function - The Hyperbolic Cosine
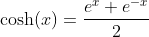
A function is called even if f(x) = f(-x)
Odd Part of the Exponential Function - The Hyperbolic Sine
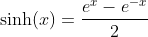
A function is called odd if f(x) = -f(-x)
Taylor Series of the Hyperbolic Cosine Function
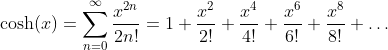
Taylor Series of the Hyperbolic Sine Function
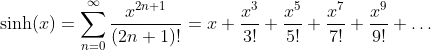
Relation between Hyperbolic Cosine Function and Cosine Function
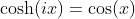
Relation between Hyperbolic Sine Function and Sine Function
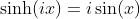
Taylor Series of the Cosine Function
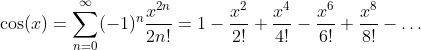
Taylor Series of the Sine Function
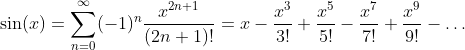
Basic Relations
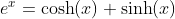
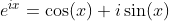
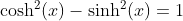
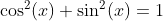
Definition of Sine and Cosine Functions with the Complex Exponential Function
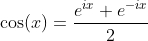
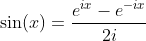
Definition of Tangent and Cotangent Functions with Sine and Cosine Functions
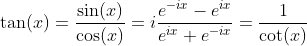
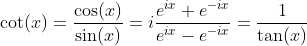
Hyperbolic Tangent and Hyperbolic Cotangent Functions
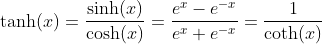
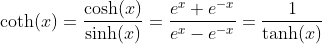
Logarithm Function: y = ln(x)
The logarithm function is defined for x values in the range 0 < x < ∞.
Taylor Series
Radius of convergence: |x| < 1 and x = 1.
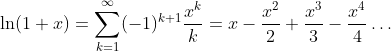
Definition with arctanh

Integral of ln(x)
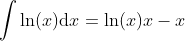
Derivative of ln(x)
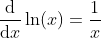
Further Properties of ln(x)
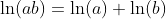
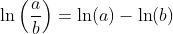
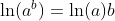
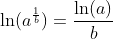
Logarithm Functions loga(x) with Different Bases
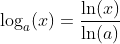
Logarithm Base 10 Function : y = log10(x) |
Logarithm Base 1/2 Function : y = log1/2(x) |
Logarithm Base 2 Function : y = log2(x) |
Logarithm loga(x) with Different Bases a
| a = 1/2 | |
| a = 2 | |
| a = e | |
| a = 10 |
Integral of the Logarithm Function: y = ln(x)x -x
Integral of ln(x)
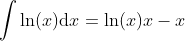
Function: y = x/ln(x)
Function
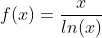
This function can be used for the approximation of the prime counting function π(x).
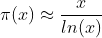
This relation is also known as prime number theorem.
Special Function
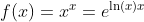
y = xx = eln(x)x
Derivative
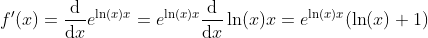
y = eln(x)x(ln(x)+1)
Gauß Function: y = e-x2
Taylor Series
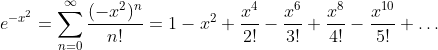
Function: y = e-1/x2
Logistic Function: y = 1/(1 + e-x)
Formulars of the logistic function:
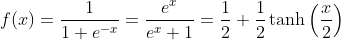
The logistic function is the solution of the logistic differential equation.
Integration of the Logistic Function
Using the substitution u = 1 + ex and u' = ex gives du = exdx.
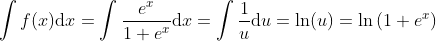
Integral of the Logistic Function: y = ln(1+ex)
Derivative of the Logistic Function
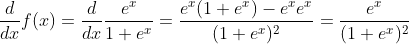
Derivative of the Logistic Function: y = ex/(1+ex)2
Bernoulli Function: x/(1 - e-x)
Bernoulli Function: x/(e-x - 1)
Bernoulli Function
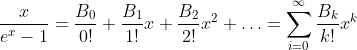
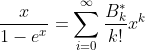
The Bi are the Bernoulli Numbers.
Bernoulli Numbers
The Bernoulli numbers Bi and Bernoulli numbers Bi* differ only in the value of i= 1. B1=-1/2 and B1* = 1/2, where they only have different sign. All the other values are the same.
| i | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | ... |
| Bi | 1 | ±1/2 | 1/6 | 0 | -1/30 | 0 | 1/42 | 0 | -1/30 | 0 | 5/66 | 0 | -291/2730 | ... |
Hyperbolic Sine Function - Sinus Hyperbolicus: y = sinh(x)
Taylor Series
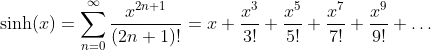
Relations
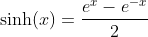
Inverse Hyperbolic Sine Function - Area Sinus Hyperbolicus: y = arsinh(x)
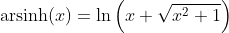
Hyperbolic Cosine Function - Cosinus Hyperbolicus: y = cosh(x)
Taylor Series
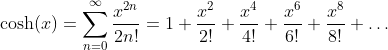
Relations
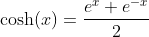
Invers Hyperbolic Cosine Function - Area Cosinus Hyperbolicus: y = arcosh(x)
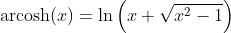
Hyperbolic Tangent Function - Tangens Hyperbolicus: y = tanh(x)
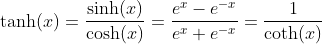
Inverse Hyperbolic Tangent Function - Area Tangens Hyperbolicus: y = artanh(x)
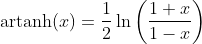
Hyperbolic Cotangent Function - Cotangens Hyperbolicus: y = coth(x)
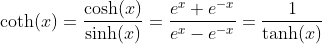
Inverse Hyperbolic Cotangent Function - Area Cotangens Hyperbolicus: y = arcoth(x)
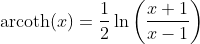
Sine Function: y = sin(x)
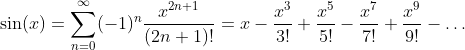
Inverse Sine Function - Arcus Sine: y = arcsin(x)
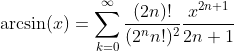
Cosine Function: y = cos(x)
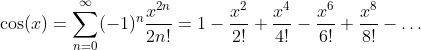
Inverse Cosine Function - Arcus Cosine: y = arccos(x)
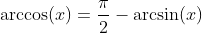
Tangent Function: y = tan(x)
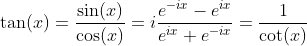
Inverse Tangent Function: y = arctan(x)
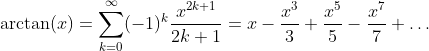
Cotangent Function: y = cot(x)
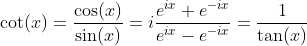
Invers Cotangent Function: y = arccot(x)
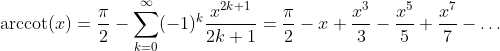
Power Functions: y = xn
y = x-4 |
y = x-3 |
y = x-2 |
y = x-1 |
y = x0 = 1 |
y = x1 = x |
y = x2 |
y = x3 |
y = x4 |
y = x5 |
y = x24 |
y = x25 |
Square Root Function: y = x1/2
Cube Root Function: y = x1/3
Next Page:
|
Home | Gallery | Physik | Philosophie | Software | Musik | Kunst | H.Wacker | Links | Inhalt |
 English
English

|
|
|
| Mathematik | Linear Algebra | Geometric Algebra | Clifford Algebra | Hypercomplex Numbers | Prime Numbers |

